GDALVector provides an interface for accessing a vector layer in a GDAL
dataset and calling methods on the underlying OGRLayer object.
An object of class GDALVector persists an open connection to the dataset,
and exposes methods to:
retrieve layer information
set attribute and spatial filters
set a list of ignored or selected columns
traverse and read feature data by traditional row-based cursor, including an analog of
DBI::dbFetch()read via column-oriented Arrow Array stream
write new features in a layer
edit/overwrite existing features
upsert
delete features
perform data manipulation within transactions.
GDALVector is a C++ class exposed directly to R (via RCPP_EXPOSED_CLASS).
Fields and methods of the class are accessed using the $ operator. Note
that all arguments to class methods are required and must be given in the
order documented. Most GDALVector methods take zero or one argument, so
this is usually not an issue. Class constructors are the main exception.
Naming the arguments is optional but may be preferred for readability.
Arguments
- dsn
Character string containing the data source name (DSN), usually a filename or database connection string.
- layer
Character string containing the name of a layer within the data source. May also be given as an SQL SELECT statement to be executed against the data source, defining a layer as the result set.
- read_only
Logical scalar.
TRUEto open the layer read-only (the default), orFALSEto open with write access.- open_options
Optional character vector of
NAME=VALUEpairs specifying dataset open options.- spatial_filter
Optional character string containing a geometry in Well Known Text (WKT) format which represents a spatial filter.
- dialect
Optional character string to control the statement dialect when SQL is used to define the layer. By default, the OGR SQL engine will be used, except for RDBMS drivers that will use their dedicated SQL engine, unless
"OGRSQL"is explicitly passed as the dialect. The"SQLITE"dialect can also be used.
Value
An object of class GDALVector, which contains pointers to the
opened layer and the GDAL dataset that owns it. Class methods that operate
on the layer are described in Details, along with a set of writable fields
for per-object settings. Values may be assigned to the class fields as
needed during the lifetime of the object (i.e., by regular <- or
= assignment).
Usage (see Details)
## Constructors
# for single-layer file formats such as shapefile
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn)
# specifying the layer name, or SQL statement defining the layer
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, layer)
# for update access
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only = FALSE)
# using dataset open options
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only, open_options)
# setting a spatial filter and/or specifying the SQL dialect
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only, open_options, spatial_filter, dialect)
## Read/write fields (per-object settings)
lyr$defaultGeomColName
lyr$returnGeomAs
lyr$promoteToMulti
lyr$convertToLinear
lyr$wkbByteOrder
lyr$arrowStreamOptions
lyr$quiet
lyr$transactionsForce
## Methods
lyr$open(read_only)
lyr$isOpen()
lyr$getDsn()
lyr$getFileList()
lyr$info()
lyr$getDriverShortName()
lyr$getDriverLongName()
lyr$getName()
lyr$getFieldNames()
lyr$testCapability()
lyr$getFIDColumn()
lyr$getGeomType()
lyr$getGeometryColumn()
lyr$getSpatialRef()
lyr$bbox()
lyr$getLayerDefn()
lyr$getFieldDomain(domain_name)
lyr$setAttributeFilter(query)
lyr$getAttributeFilter()
lyr$setIgnoredFields(fields)
lyr$setSelectedFields(fields)
lyr$getIgnoredFields()
lyr$setSpatialFilter(wkt)
lyr$setSpatialFilterRect(bbox)
lyr$getSpatialFilter()
lyr$clearSpatialFilter()
lyr$getFeatureCount()
lyr$getNextFeature()
lyr$setNextByIndex(i)
lyr$getFeature(fid)
lyr$resetReading()
lyr$fetch(n)
lyr$getArrowStream()
lyr$releaseArrowStream()
lyr$setFeature(feature)
lyr$createFeature(feature)
lyr$batchCreateFeature(feature_set)
lyr$upsertFeature(feature)
lyr$getLastWriteFID()
lyr$deleteFeature(fid)
lyr$syncToDisk()
lyr$startTransaction()
lyr$commitTransaction()
lyr$rollbackTransaction()
lyr$getMetadata()
lyr$setMetadata(metadata)
lyr$getMetadataItem(mdi_name)
lyr$close()Details
Constructors
new(GDALVector, dsn)
The first layer by index is assumed if the layer argument is omitted, so
this form of the constructor might be used for single-layer formats like
shapefile.
new(GDALVector, dsn, layer)
Constructor specifying the name of a layer to open. The layer argument
may also be given as an SQL SELECT statement to define a layer as the result
set.
new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only)
Constructor specifying read/write access (read_only = TRUE|FALSE).
The layer argument is required in this form of the constructor, but may be
given as empty string (""), in which case the first layer by index will be
assumed.
new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only, open_options)
Constructor specifying dataset open options as a character vector of
NAME=VALUE pairs.
new(GDALVector, dsn, layer, read_only, open_options, spatial_filter, dialect))
Constructor to specify a spatial filter and/or SQL dialect. All arguments
are required in this form of the constructor, but open_options may be
NULL, and spatial_filter or dialect may be an empty string ("").
Read/write fields
$defaultGeomColName
Character string specifying a name to use for returned columns when the
geometry column name in the source layer is empty, like with shapefiles etc.
Defaults to "geom".
$returnGeomAs
Character string specifying the return format of feature geometries.
Must be one of WKB (the default), WKB_ISO, WKT, WKT_ISO, BBOX, or
NONE.
Using WKB/WKT exports as 99-402 extended dimension (Z) types for Point,
LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon and
GeometryCollection. For other geometry types, it is equivalent to using
WKB_ISO/WKT_ISO (see https://libgeos.org/specifications/wkb/).
Using BBOX exports as a list of numeric vectors, each of length 4 with
values xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax. If an empty geometry is encountered these
values will be NA_real_ in the corresponding location.
Using NONE will result in no geometry value being present in the feature
returned.
$promoteToMulti
A logical value specifying whether to automatically promote geometries from
Polygon to MultiPolygon, Point to MultiPoint, or LineString to
MultiLineString during read operations (i.e., with methods
$getFeature(), $getNextFeature(), $fetch()).
Defaults to FALSE. Setting to TRUE may be useful when reading from
layers such as shapefiles that mix Polygons and MultiPolygons.
$convertToLinear
A logical value specifying whether to convert non-linear geometry types into
linear geometry types by approximating them (i.e., during read operations
with methods $getFeature(), $getNextFeature(),
$fetch()). Defaults to FALSE. If set to TRUE, handled conversions
are:
wkbCurvePolygon -> wkbPolygon
wkbCircularString -> wkbLineString
wkbCompoundCurve -> wkbLineString
wkbMultiSurface -> wkbMultiPolygon
wkbMultiCurve -> wkbMultiLineString
$wkbByteOrder
Character string specifying the byte order for WKB geometries.
Must be either LSB (Least Significant Byte first, the default) or
MSB (Most Significant Byte first).
$arrowStreamOptions
Character vector of "NAME=VALUE" pairs giving options used by the
$getArrowStream() method (see below). The available options may be
driver and GDAL version specific. Options available as of GDAL 3.8 are
listed below. For more information about options for Arrow stream, see
the GDAL API documentation for
OGR_L_GetArrowStream().
INCLUDE_FID=YES/NO. Defaults to YES.
MAX_FEATURES_IN_BATCH=integer. Maximum number of features to retrieve in an ArrowArray batch. Defaults to 65536.
TIMEZONE=unknown/UTC/(+|:)HH:MM or any other value supported by Arrow (GDAL >= 3.8).
GEOMETRY_METADATA_ENCODING=OGC/GEOARROW (GDAL >= 3.8). The GDAL default is OGC if not specified.
GEOMETRY_ENCODING=WKB (Arrow/Parquet drivers). To force a fallback to the generic implementation when the native geometry encoding is not WKB. Otherwise the geometry will be returned with its native Arrow encoding (possibly using GeoArrow encoding).
$quiet
A logical value, FALSE by default. Set to TRUE to suppress various
messages and warnings.
$transactionsForce
A logical value, FALSE by default. Affects the behavior of attempted
transactions on the layer (see the $startTransaction() method below).
By default, only "efficient" transactions will be attempted. Some drivers
may offer an emulation of transactions, but sometimes with significant
overhead, in which case the user must explicitly allow for such an
emulation by first setting $transactionsForce <- TRUE.
Methods
$open(read_only)
(Re-)opens the vector layer on the existing DSN. Use this method to
open a layer that has been closed using $close(). May be used to
re-open a layer with a different read/write access (read_only set to
TRUE or FALSE). The method will first close an open dataset, so it is
not required to call $close() explicitly in this case.
No return value, called for side effects.
$isOpen()
Returns a logical value indicating whether the vector dataset is open.
$getDsn()
Returns a character string containing the dsn associated with this
GDALVector object (dsn originally used to open the layer).
$getFileList()
Returns a character vector of files believed to be part of the data source.
If it returns an empty string ("") it means there is believed to be no
local file system files associated with the dataset (e.g., a virtual file
system). The returned filenames will normally be relative or absolute
paths depending on the path used to originally open the dataset.
$info()
Prints information about the vector layer to the console (no
return value, called for that side effect only).
For non-SQL DSN/layer, calls ogrinfo() passing the command options
cl_arg = c("-so", "-nomd"), and for layers open with a SQL statement,
calls ogrinfo() passing the command options
cl_arg = c("-so", "-nomd", "-sql", <statement>).
$getDriverShortName()
Returns the short name of the vector format driver.
$getDriverLongName()
Returns the long name of the vector format driver.
$getName()
Returns the layer name.
$getFieldNames()
Returns a character vector of the layer's field names.
$testCapability()
Tests whether the layer supports named capabilities based on the current
read/write access. Returns a list of capabilities with values TRUE or
FALSE. The returned list contains the following named elements:
RandomRead, SequentialWrite, RandomWrite, UpsertFeature,
FastSpatialFilter, FastFeatureCount, FastGetExtent,
FastSetNextByIndex, FastGetArrowStream, FastWriteArrowBatch,
CreateField, CreateGeomField, DeleteField, ReorderFields,
AlterFieldDefn, AlterGeomFieldDefn, DeleteFeature, StringsAsUTF8,
Transactions, CurveGeometries.
Note that some layer capabilities are GDAL version dependent and may not
be listed if not supported by the GDAL version currently in use.
(See the GDAL documentation for
OGR_L_TestCapability().)
$getFIDColumn()
Returns the name of the underlying database column being used as the FID
column, or empty string ("") if not supported.
$getGeomType()
Returns the well known name of the layer geometry type as character string.
For layers with multiple geometry fields, this method only returns the
geometry type of the first geometry column. For other columns, use
$getLayerDefn(). For layers without any geometry field, this method
returns "NONE".
$getGeometryColumn()
Returns he name of the underlying database column being used as the geometry
column, or an empty string ("") if not supported.
For layers with multiple geometry fields, this method only returns the
name of the first geometry column. For other columns, use method
$getLayerDefn().
$getSpatialRef()
Returns a WKT string containing the spatial reference system for this layer,
or empty string ("") if no spatial reference exists.
$bbox()
Returns a numeric vector of length four containing the bounding box
for this layer (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax). Note that bForce = true is set in
the underlying API call to OGR_L_GetExtent(), so the entire layer may be
scanned to compute a minimum bounding rectangle (see FastGetExtent in the
list returned by $testCapability()). Depending on the format driver,
a spatial filter may or may not be taken into account, so it is safer to
call $bbox() without setting a spatial filter.
$getLayerDefn()
Returns a list containing the OGR feature class definition for this layer
(a.k.a. layer definition). The list contains zero or more attribute field
definitions, along with one or more geometry field definitions.
See ogr_define for details of the field and feature class definitions.
$getFieldDomain(domain_name)
Returns a list containing the definition of the OGR field domain with the
passed domain_name, or NULL if domain_name is not found.
See ogr_define for specification of the list containing a field domain
definition.
Some formats support the use of field domains which describe the valid values
that can be stored in a given attribute field, e.g., coded values that are
present in a specified enumeration, values constrained to a specified
range, or values that must match a specified pattern.
See
https://gdal.org/en/stable/user/vector_data_model.html#field-domains.
Requires GDAL >= 3.3.
$setAttributeFilter(query)
Sets an attribute query string to be used when fetching features via the
$getNextFeature() or $fetch() methods.
Only features for which query evaluates as true will be returned.
The query string should be in the format of an SQL WHERE clause, described
in the "WHERE"
section of the OGR SQL dialect documentation (e.g.,
"population > 1000000 and population < 5000000", where population is an
attribute in the layer).
In some cases (RDBMS backed drivers, SQLite, GeoPackage) the native
capabilities of the database may be used to to interpret the WHERE clause,
in which case the capabilities will be broader than those of OGR SQL.
Note that installing a query string will generally result in resetting the
current reading position (as with $resetReading() described below).
The query parameter may be set to empty string ("") to clear the current
attribute filter.
$getAttributeFilter()
Returns the attribute query string currently in use, or empty string ("")
if an attribute filter is not set.
$setIgnoredFields(fields)
Set which fields can be omitted when retrieving features from the layer.
The fields argument is a character vector of field names. Passing an
empty string ("") for fields will reset to no ignored fields.
If the format driver supports this functionality (testable using
$testCapability()$IgnoreFields), it will not fetch the specified
fields in subsequent calls to $getFeature() / $getNextFeature()
/ $fetch(), and thus save some processing time and/or bandwidth.
Besides field names of the layer, the following special fields can be passed:
"OGR_GEOMETRY" to ignore geometry and "OGR_STYLE" to ignore layer style.
By default, no fields are ignored. Note that fields that are used in an
attribute filter should generally not be set as ignored fields, as most
drivers (such as those relying on the OGR SQL engine) will be unable to
correctly evaluate the attribute filter. No return value, called for side
effects.
$setSelectedFields(fields)
Set which fields will be included when retrieving features from the layer.
The fields argument is a character vector of field names. Passing an
empty string ("") for fields will reset to no ignored fields.
See the $setIgnoredFields() method above for more information. The
data source must provide IgnoreFields capability in order to set selected
fields. Note that geometry fields, if desired, must be specified when setting
selected fields, either by including named geometry field(s) or the special
field "OGR_GEOMETRY" in the fields argument.
No return value, called for side effects.
$getIgnoredFields()
Returns a character vector containing the list of currently ignored fields,
or an empty vector (character(0)) if no fields are currently set to
ignored (or if the format driver does not support ignored fields).
$setSpatialFilter(wkt)
Sets a new spatial filter from a geometry in WKT format. This method sets
the geometry to be used as a spatial filter when fetching features via the
$getNextFeature() or $fetch() methods. Only features that
geometrically intersect the filter geometry will be returned. Currently this
test may be inaccurately implemented (depending on the vector format driver),
but it is guaranteed that all features whose envelope overlaps the envelope
of the spatial filter will be returned. This can result in more shapes being
returned that should strictly be the case.
wkt is a character string containing a WKT geometry in the same coordinate
system as the layer. An empty string ("") may be passed indicating that
the current spatial filter should be cleared, but no new one instituted.
$setSpatialFilterRect(bbox)
Sets a new rectangular spatial filter. This method sets a rectangle to be
used as a spatial filter when fetching features via the
$getNextFeature() or $fetch() methods.
Only features that geometrically intersect the given rectangle will be
returned.
bbox is a numeric vector of length four containing xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
in the same coordinate system as the layer as a whole (as returned by
$getSpatialRef()).
$getSpatialFilter()
Returns the current spatial filter geometry as a WKT string, or empty string
("") if a spatial filter is not set.
$clearSpatialFilter()
Clears a spatial filter that was set with $setSpatialFilterRect().
No return value, called for that side effect.
$getFeatureCount()
Returns the number of features in the layer. For dynamic databases the count
may not be exact. This method forces a count in the underlying API call
(i.e., bForce = TRUE in the call to OGR_L_GetFeatureCount()). Note that
some vector drivers will actually scan the entire layer once to count
features. The FastFeatureCount element in the list returned by
the $testCapability() method can be checked if this might be a
concern.
The number of features returned takes into account the spatial and/or
attribute filters. Some driver implementations of this method may alter the
read cursor of the layer.
$getNextFeature()
Fetch the next available feature from this layer. Only features matching the
current spatial and/or attribute filter (if defined) will be returned.
This method implements sequential access to the features of a layer.
The $resetReading() method can be used to start at the beginning
again.
Returns a list with the unique feature identifier (FID), the attribute and
geometry field names, and their values. The returned list carries the
OGRFeature class attribute with S3 methods for for print() and plot().
NULL is returned if no more features are available.
$setNextByIndex(i)
Moves the read cursor to feature i in the current result set
(with 0-based indexing).
This method allows positioning of a layer such that a call to
$getNextFeature() or $fetch() will read the requested
feature(s), where i is an absolute index into the current result set.
So, setting i = 3 would mean the next feature read with
$getNextFeature() would have been the fourth feature read if
sequential reading took place from the beginning of the layer, including
accounting for spatial and attribute filters.
This method is not implemented efficiently by all vector format drivers. The
default implementation simply resets reading to the beginning and then calls
GetNextFeature() i times.
To determine if fast seeking is available on the current layer, check
the FastSetNextByIndex element in the list returned by the
$testCapability() method. No return value, called for side effect.
$getFeature(fid)
Returns a feature by its identifier. The value of fid must be a numeric
value, optionally carrying the bit64::integer64 class attribute.
Success or failure of this operation is unaffected by any spatial or
attribute filters that may be in effect.
The RandomRead element in the list returned by $testCapability() can
be checked to establish if this layer supports efficient random access
reading; however, the call should always work if the feature exists since a
fallback implementation just scans all the features in the layer looking for
the desired feature. Returns a list with the unique feature identifier (FID),
the attribute and geometry field names, and their values, or NULL on
failure. Note that sequential reads (with $getNextFeature()) are
generally considered interrupted by a call to $getFeature().
$resetReading()
Reset feature reading to start on the first feature. No return value, called
for that side effect.
$fetch(n)
Fetches the next n features from the layer and returns them as a data
frame. This allows retrieving the entire set of features, one page of
features at a time, or the remaining features (from the current cursor
position). Returns a data frame with as many rows as features were fetched,
and as many columns as attribute plus geometry fields in the result set,
even if the result is a single value or has one or zero rows.
The returned data frame carries the OGRFeatureSet class attribute with S3
methods for for print() and plot().
This method is an analog of
DBI::dbFetch().
The n argument is the maximum number of features to retrieve per fetch
given as integer or numeric but assumed to be a whole number (will
be truncated). Use n = -1 or n = Inf to retrieve all pending features
(resets reading to the first feature).
Otherwise, $fetch() can be called multiple times to perform forward
paging from the current cursor position. Passing n = NA is also supported
and returns the remaining features.
Fetching zero features is possible to retrieve the structure of the feature
set as a data frame (columns fully typed).
OGR field types are returned as the following R types (type-specific NA
for OGR NULL values):
OFTInteger:
integervalueOFTInteger subtype OFSTBoolean:
logicalvalueOFTIntegerList: vector of
integer(list column)OFTInteger64:
numericvalue carrying the"integer64"class attributeOFTInteger64 subtype OFSTBoolean:
logicalvalueOFTInteger64List: vector of
bit64::integer64(list column)OFTReal:
numericvalueOFTRealList: vector of
numeric(list column)OFTString:
characterstringOFTStringList: vector of
characterstrings (list column)OFTDate:
numericvalue of class"Date"OFTDateTime:
numericvalue of class"POSIXct"(millisecond accuracy)OFTTime:
characterstring ("HH:MM:SS")OFTBinary:
rawvector (list column,NULLentries for OGR NULL values)
Geometries are not returned if the field returnGeomAs is set to NONE.
Omitting the geometries may be beneficial for performance and memory usage
when access only to feature attributes is needed. Geometries are returned
as raw vectors in a data frame list column when returnGeomAs is set to
WKB (the default) or WKB_ISO, or as character strings when
returnGeomAs is set to one of WKT or WKT_ISO.
Note that $getFeatureCount() is called internally when fetching the
full feature set or all remaining features (but not for a page of features).
$getArrowStream()
Returns a nanoarrow_array_stream object exposing an Arrow C stream on the
layer (requires GDAL >= 3.6).
The writable field $arrowStreamOptions can be used to set options
before calling this method (see above). An error is raised if an array stream
on the layer cannot be obtained.
Generally, only one ArrowArrayStream can be active at a time on a given
layer (i.e., the last active one must be explicitly released before a next
one is asked). Changing attribute or spatial filters, ignored columns,
modifying the schema or using $resetReading() /
$getNextFeature() while using an ArrowArrayStream is strongly
discouraged and may lead to unexpected results. As a rule of thumb, no
OGRLayer methods that affect the state of a layer should be called on the
layer while an ArrowArrayStream on it is active. Methods available on the
stream object are: $get_schema(), $get_next() and
$release() (see Examples).
The stream should be released once reading is complete. Calling the release method as soon as you can after consuming a stream is recommended by the nanoarrow documentation.
See also the $testCapability() method above to check whether the
format driver provides a specialized implementation (FastGetArrowStream),
as opposed to the (slower) default implementation. Note however that
specialized implementations may fallback to the default when attribute or
spatial filters are in use.
(See the GDAL documentation for
OGR_L_GetArrowStream().)
$releaseArrowStream()
Releases the Arrow C stream returned by $getArrowStream() and clears
the nanoarrow_array_stream object (if GDAL >= 3.6, otherwise does nothing).
This is equivalent to calling the $release() method on the
nanoarrow_array_stream object. No return value, called for side effects.
$setFeature(feature)
Rewrites/replaces an existing feature. This method writes a feature based on
the feature id within the input feature. The feature argument is a named
list of fields and their values, and must include a FID element
referencing the existing feature to rewrite. The RandomWrite element in
the list returned by $testCapability() can be checked to establish if
this layer supports random access writing via $setFeature().
The way omitted fields in the passed feature are processed is driver
dependent:
SQL-based drivers which implement set feature through SQL UPDATE will skip unset fields, and thus the content of the existing feature will be preserved.
The shapefile driver will write a NULL value in the DBF file.
The GeoJSON driver will take into account unset fields to remove the corresponding JSON member.
Returns logical TRUE upon successful completion, or FALSE if setting the
feature did not succeed. The FID of the last feature written to the layer
may be obtained with the method $getLastWriteFID() (see below).
To set a feature, but create it if it doesn't exist see the
$upsertFeature() method.
$createFeature(feature)
Creates and writes a new feature within the layer. The feature argument is
a named list of fields and their values (might be one row of a data frame).
The passed feature is written to the layer as a new feature, rather than
overwriting an existing one. If the feature has a FID element with other
than NA (i.e., a numeric value, optionally carrying the bit64::integer64
class attribute and assumed to be a whole number), then the format
driver may use that as the feature id of the new feature, but not
necessarily. The FID of the last feature written to the layer may be
obtained with the method $getLastWriteFID() (see below).
Returns logical TRUE upon successful completion, or FALSE if creating
the feature did not succeed. To create a feature, but set it if it already
exists see the $upsertFeature() method.
$batchCreateFeature(feature_set)
Batch version of $createFeature(). Creates and writes a batch of new
features within the layer from input passed as a data frame in the
feature_set argument. Column names in the data frame must match field
names of the layer and have compatible data types. The specifications
listed above under the $fetch() method generally apply to input data
types for writing, but integers may be passed as 'numeric', and
the 'integer64' class attribute is not strictly required on 'numeric'
input if it is not needed for the data being passed to an OFTInteger64
field.
Returns a logical vector of length equal to the number of input features
(rows of the data frame), with TRUE indicating success for the feature at
that row index, or FALSE if writing the feature failed.
It is recommended to use transactions when batch writing features to a
layer (see $startTransaction() below). This will generally give large
performance benefit with data sources that provide efficient transaction
support (e.g., RDBMS-based sources such as GeoPackage and PostGIS). In
addition, the return value of $batchCreateFeature() can be checked,
and the transaction optionally committed or rolled back based on results of
the operation across the full set of input features.
$upsertFeature(feature)
Rewrites/replaces an existing feature or creates a new feature within the
layer. This method will write a feature to the layer, based on the feature
id within the input feature. The feature argument is a named list of
fields and their values (might be one row of a data frame), potentially
including a FID element referencing an existing feature to rewrite. If
the feature id doesn't exist a new feature will be written. Otherwise, the
existing feature will be rewritten.
The UpsertFeature element in the list returned by $testCapability()
can be checked to determine if this layer supports upsert writing. See
$setFeature() above for a description of how omitted fields in the
passed feature are processed.
Returns logical TRUE upon successful completion, or FALSE if upsert did
not succeed. Requires GDAL >= 3.6.
$getLastWriteFID()
Returns the FID of the last feature written (either newly created or updated
existing). NULL is returned if no features have been written in the layer.
Note that OGRNullFID (-1) may be returned after writing a feature in some
formats. This is the case if a FID has not been assigned yet, and generally
does not indicate an error (e.g., formats that do not store a persistent FID
and assign FIDs upon a sequential read operation). The returned FID is a
numeric value carrying the bit64::integer64 class attribute.
$deleteFeature(fid)
Deletes a feature from the layer. The feature with the indicated feature ID
is deleted from the layer if supported by the format driver. The value of
fid must be a numeric value, optionally carrying the bit64::integer64
class attribute (should be a whole number, will be truncated).
The DeleteFeature element in the list returned by $testCapability()
can be checked to establish if this layer has delete feature capability.
Returns logical TRUE if the operation succeeds, or FALSE on failure.
$syncToDisk()
Flushes pending changes to disk. This call is intended to force the layer to
flush any pending writes to disk, and leave the disk file in a consistent
state. It would not normally have any effect on read-only datasources. Some
formats do not implement this method, and will still return no error. An
error is only returned if an error occurs while attempting to flush to disk.
In any event, you should always close any opened datasource with
$close() which will ensure all data is correctly flushed. Returns
logical TRUE if no error occurs (even if nothing is done) or FALSE on
error.
$startTransaction()
Creates a transaction if supported by the vector data source. By default,
only "efficient" transactions will be attempted. See the writable field
$transactionsForce above, which must be set to TRUE to allow for
emulated transactions. These are supported by some drivers but with
potentially significant overhead. The function ogr_ds_test_cap() can be
used to determine whether a vector data source supports efficient or
emulated transactions.
All changes done after the start of the transaction are definitely applied
in the data source if $commitTransaction() is called. They can be
canceled by calling $rollbackTransaction() instead.
Nested transactions are not supported. Transactions are implemented at the
dataset level, so multiple GDALVector objects using the same data source
should not have transactions active at the same time.
In case $startTransaction() fails, neither $commitTransaction()
nor $rollbackTransaction() should be called.
If an error occurs after a successful $startTransaction(), the whole
transaction may or may not be implicitly canceled, depending on the format
driver (e.g., the PostGIS driver will cancel it, SQLite/GPKG will not). In
any case, in the event of an error, an explicit call to
$rollbackTransaction() should be done to keep things balanced.
Returns logical TRUE if the transaction is created, or FALSE on failure.
$commitTransaction()
Commits a transaction if supported by the vector data source.
Returns a logical value, TRUE if the transaction is successfully committed.
Returns FALSE if no transaction is active, or the rollback fails, or if the
data source does not support transactions.
Depending on the format driver, this may or may not abort layer sequential
reading that may be active.
$rollbackTransaction()
Rolls back a data source to its state before the start of the current
transaction, if transactions are supported by the data source.
Returns a logical value, TRUE if the transaction is successfully rolled
back. Returns FALSE if no transaction is active, or the rollback fails,
or if the data source does not support transactions.
$getMetadata()
Returns a character vector of all metadata NAME=VALUE pairs for the
layer or empty string ("") if there are no metadata items.
$setMetadata(metadata)
Sets metadata on the layer if the format supports it. The metadata
argument is given as a character vector of NAME=VALUE pairs.
Returns logical TRUE on success or FALSE if metadata could
not be set.
$getMetadataItem(mdi_name)
Returns the value of a specific metadata item named mdi_name, or empty
string ("") if no matching item is found.
$close()
Closes the vector dataset (no return value, called for side effects).
Calling $close() results in proper cleanup, and flushing of any
pending writes.
The GDALVector object is still available after calling $close().
The layer can be re-opened on the existing dsn with
$open(read_only = TRUE|FALSE).
See also
ogr_define, ogr_manage, ogr2ogr(), ogrinfo()
GDAL vector format descriptions:
https://gdal.org/en/stable/drivers/vector/index.html
GDAL-supported SQL dialects:
https://gdal.org/en/stable/user/ogr_sql_sqlite_dialect.html
GDAL Vector API documentation:
https://gdal.org/en/stable/api/index.html
Examples
## MTBS fire perimeters in Yellowstone National Park 1984-2022
f <- system.file("extdata/ynp_fires_1984_2022.gpkg", package = "gdalraster")
## copy to a temporary file that is writeable
dsn <- file.path(tempdir(), basename(f))
file.copy(f, dsn)
#> [1] TRUE
(lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, "mtbs_perims"))
#> C++ object of class GDALVector
#> Driver : GeoPackage (GPKG)
#> DSN : /tmp/RtmpO4j4Ij/ynp_fires_1984_2022.gpkg
#> Layer : mtbs_perims
#> CRS : NAD83 / Montana (EPSG:32100)
#> Geom : MULTIPOLYGON
str(lyr)
#> Reference class 'Rcpp_GDALVector' [package "gdalraster"] with 11 fields
#> $ arrowStreamOptions: chr ""
#> $ convertToLinear : logi FALSE
#> $ defaultGeomColName: chr "geom"
#> $ m_dialect : chr ""
#> $ m_is_sql : logi FALSE
#> $ m_layer_name : chr "mtbs_perims"
#> $ promoteToMulti : logi FALSE
#> $ quiet : logi FALSE
#> $ returnGeomAs : chr "WKB"
#> $ transactionsForce : logi FALSE
#> $ wkbByteOrder : chr "LSB"
#> and 73 methods, of which 59 are possibly relevant:
#> OGRFeatureFromList_dumpReadble, batchCreateFeature, bbox,
#> clearSpatialFilter, close, commitTransaction, createFeature, deleteFeature,
#> fetch, finalize, getArrowStream, getAttributeFilter, getDriverLongName,
#> getDriverShortName, getDsn, getFIDColumn, getFeature, getFeatureCount,
#> getFieldDomain, getFieldNames, getFileList, getGeomType, getGeometryColumn,
#> getIgnoredFields, getLastWriteFID, getLayerDefn, getMetadata,
#> getMetadataItem, getName, getNextFeature, getSpatialFilter, getSpatialRef,
#> info, initialize, isOpen, layerClip, layerErase, layerIdentity,
#> layerIntersection, layerSymDifference, layerUnion, layerUpdate, open,
#> releaseArrowStream, resetReading, rollbackTransaction, setAttributeFilter,
#> setFeature, setIgnoredFields, setMetadata, setNextByIndex,
#> setSelectedFields, setSpatialFilter, setSpatialFilterRect, show#envRefClass,
#> startTransaction, syncToDisk, testCapability, upsertFeature
## dataset info
lyr$getDriverShortName()
#> [1] "GPKG"
lyr$getDriverLongName()
#> [1] "GeoPackage"
lyr$getFileList()
#> [1] "/tmp/RtmpO4j4Ij/ynp_fires_1984_2022.gpkg"
## layer info
lyr$getName()
#> [1] "mtbs_perims"
lyr$getGeomType()
#> [1] "MULTIPOLYGON"
lyr$getGeometryColumn()
#> [1] "geom"
lyr$getFIDColumn()
#> [1] "fid"
lyr$getSpatialRef()
#> [1] "PROJCS[\"NAD83 / Montana\",GEOGCS[\"NAD83\",DATUM[\"North_American_Datum_1983\",SPHEROID[\"GRS 1980\",6378137,298.257222101,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7019\"]],AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"6269\"]],PRIMEM[\"Greenwich\",0,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"8901\"]],UNIT[\"degree\",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"9122\"]],AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"4269\"]],PROJECTION[\"Lambert_Conformal_Conic_2SP\"],PARAMETER[\"latitude_of_origin\",44.25],PARAMETER[\"central_meridian\",-109.5],PARAMETER[\"standard_parallel_1\",49],PARAMETER[\"standard_parallel_2\",45],PARAMETER[\"false_easting\",600000],PARAMETER[\"false_northing\",0],UNIT[\"metre\",1,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"9001\"]],AXIS[\"Easting\",EAST],AXIS[\"Northing\",NORTH],AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"32100\"]]"
lyr$bbox()
#> [1] 469685.73 -12917.76 573531.72 96577.34
## layer capabilities
lyr$testCapability()
#> $RandomRead
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $SequentialWrite
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $RandomWrite
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $UpsertFeature
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $FastSpatialFilter
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $FastFeatureCount
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $FastGetExtent
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $FastSetNextByIndex
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $FastGetArrowStream
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $FastWriteArrowBatch
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $CreateField
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $CreateGeomField
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $DeleteField
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $ReorderFields
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $AlterFieldDefn
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $AlterGeomFieldDefn
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $IgnoreFields
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $DeleteFeature
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $Rename
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $StringsAsUTF8
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $CurveGeometries
#> [1] TRUE
#>
## re-open with write access
lyr$open(read_only = FALSE)
lyr$testCapability()$SequentialWrite
#> [1] TRUE
lyr$testCapability()$RandomWrite
#> [1] TRUE
## feature class definition - a list of field names and their definitions
defn <- lyr$getLayerDefn()
names(defn)
#> [1] "event_id" "incid_name" "incid_type" "map_id" "burn_bnd_ac"
#> [6] "burn_bnd_lat" "burn_bnd_lon" "ig_date" "ig_year" "geom"
str(defn)
#> List of 10
#> $ event_id :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTString"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 254
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ incid_name :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTString"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 254
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ incid_type :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTString"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 254
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ map_id :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTInteger64"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 0
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ burn_bnd_ac :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTInteger64"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 0
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ burn_bnd_lat:List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTString"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 10
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ burn_bnd_lon:List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTString"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 10
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ ig_date :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTDate"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 0
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ ig_year :List of 9
#> ..$ type : chr "OFTInteger"
#> ..$ subtype : chr "OFSTNone"
#> ..$ width : int 0
#> ..$ precision : int 0
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_unique : logi FALSE
#> ..$ default : chr ""
#> ..$ domain : chr ""
#> ..$ is_geom : logi FALSE
#> $ geom :List of 4
#> ..$ type : chr "MULTIPOLYGON"
#> ..$ srs : chr "PROJCS[\"NAD83 / Montana\",GEOGCS[\"NAD83\",DATUM[\"North_American_Datum_1983\",SPHEROID[\"GRS 1980\",6378137,2"| __truncated__
#> ..$ is_nullable: logi TRUE
#> ..$ is_geom : logi TRUE
## default value of the read/write field 'returnGeomAs'
lyr$returnGeomAs
#> [1] "WKB"
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 61
## sequential read cursor
# a single feature returned as a named list of fields and their values:
(feat <- lyr$getNextFeature())
#> OGR feature
#> $FID
#> integer64
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $event_id
#> [1] WY4413411069519870807
#>
#> $incid_name
#> [1] POLECAT
#>
#> $incid_type
#> [1] Wildfire
#>
#> $map_id
#> integer64
#> [1] 10015934
#>
#> $burn_bnd_ac
#> integer64
#> [1] 1093
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lat
#> [1] 44.132
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lon
#> [1] -110.696
#>
#> $ig_date
#> [1] 1987-08-07
#>
#> $ig_year
#> [1] 1987
#>
#> $geom
#> [1] WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#>
## set an attribute filter
lyr$setAttributeFilter("ig_year = 2020")
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 1
feat <- lyr$getNextFeature()
plot(feat)
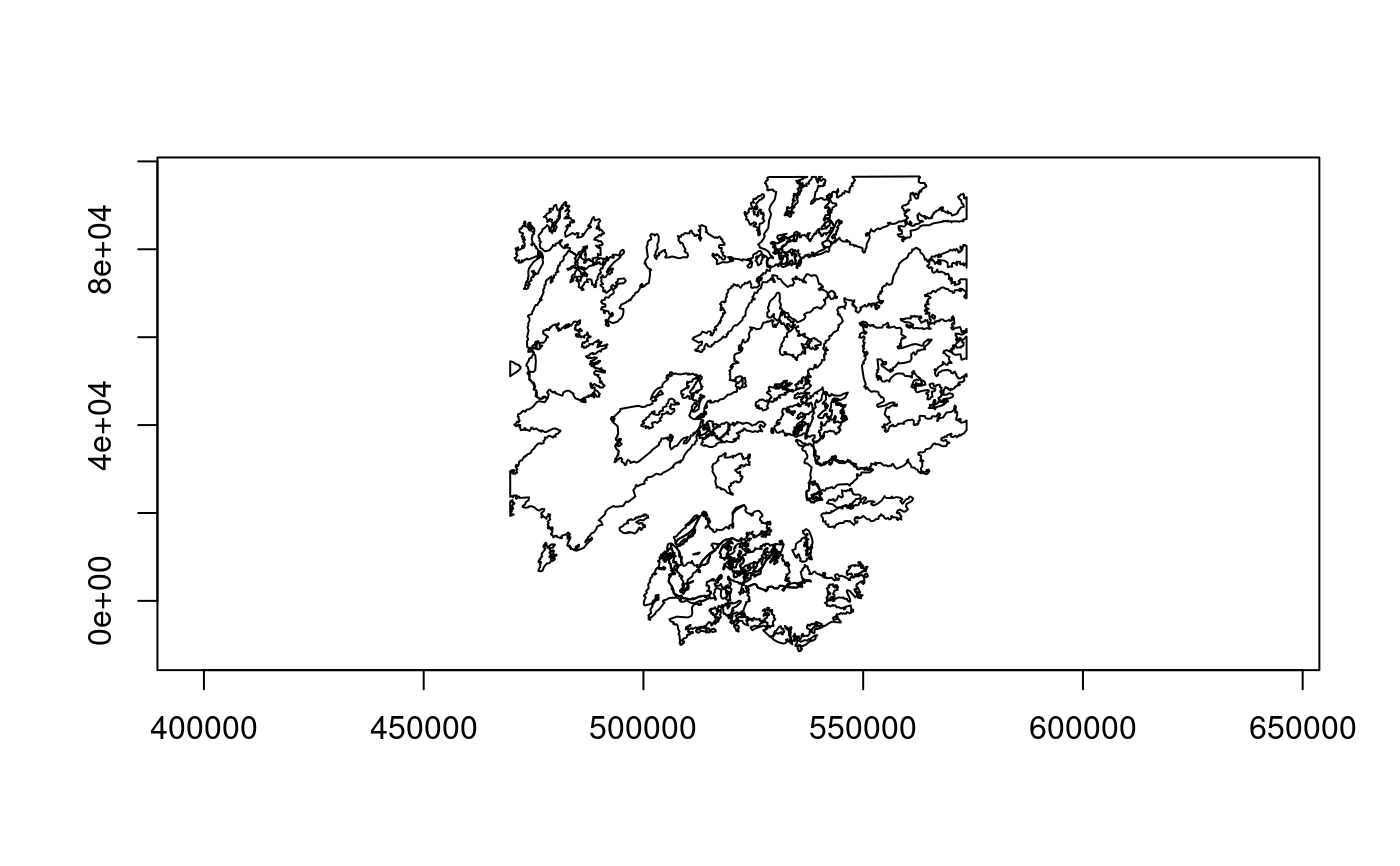 ## NULL when no more features are available
lyr$getNextFeature()
#> NULL
## reset reading to the start
lyr$resetReading()
lyr$getNextFeature()
#> OGR feature
#> $FID
#> integer64
#> [1] 61
#>
#> $event_id
#> [1] WY4438911082120200822
#>
#> $incid_name
#> [1] LONE STAR
#>
#> $incid_type
#> [1] Wildfire
#>
#> $map_id
#> integer64
#> [1] 10020495
#>
#> $burn_bnd_ac
#> integer64
#> [1] 3348
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lat
#> [1] 44.4
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lon
#> [1] -110.782
#>
#> $ig_date
#> [1] 2020-08-22
#>
#> $ig_year
#> [1] 2020
#>
#> $geom
#> [1] WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#>
## clear the attribute filter
lyr$setAttributeFilter("")
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 61
## set a spatial filter
## get the bounding box of the largest 1988 fire and use as spatial filter
## first set a temporary attribute filter to do the lookup
lyr$setAttributeFilter("ig_year = 1988 ORDER BY burn_bnd_ac DESC")
(feat <- lyr$getNextFeature())
#> OGR feature
#> $FID
#> integer64
#> [1] 7
#>
#> $event_id
#> [1] WY4470811082119880722
#>
#> $incid_name
#> [1] NORTH FORK
#>
#> $incid_type
#> [1] Wildfire
#>
#> $map_id
#> integer64
#> [1] 10014217
#>
#> $burn_bnd_ac
#> integer64
#> [1] 563527
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lat
#> [1] 44.678
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lon
#> [1] -110.716
#>
#> $ig_date
#> [1] 1988-07-22
#>
#> $ig_year
#> [1] 1988
#>
#> $geom
#> [1] WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#>
bbox <- g_wk2wk(feat$geom) |> bbox_from_wkt()
## set spatial filter on the full layer
lyr$setAttributeFilter("") # clears the attribute filter
lyr$setSpatialFilterRect(bbox)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 40
## fetch in chunks and return as data frame (class OGRFeatureSet)
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
head(feat_set)
#> OGR feature set
#> FID event_id incid_name incid_type map_id
#> 1 38 MT4471311115120070627 MADISON ARM Wildfire 16113
#> 2 7 WY4470811082119880722 NORTH FORK Wildfire 10014217
#> 3 32 MT4491211108020030820 RATHBONE Wildfire 13014
#> 4 25 WY4433011103020000816 SPRUCE COMPLEX (PLATEAU) Wildfire 10014141
#> 5 6 WY4499211096519880625 FAN Wildland Fire Use 10014215
#> 6 40 MT4502711102920070720 OWL Wildfire 16428
#> burn_bnd_ac burn_bnd_lat burn_bnd_lon ig_date ig_year
#> 1 3564 44.713 -111.151 2007-06-27 2007
#> 2 563527 44.678 -110.716 1988-07-22 1988
#> 3 2701 44.912 -111.080 2003-08-20 2003
#> 4 2808 44.329 -111.027 2000-08-16 2000
#> 5 20422 44.994 -110.976 1988-06-25 1988
#> 6 2175 45.027 -111.029 2007-07-20 2007
#> geom
#> 1 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 2 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 3 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 4 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 5 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 6 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
plot(feat_set)
## NULL when no more features are available
lyr$getNextFeature()
#> NULL
## reset reading to the start
lyr$resetReading()
lyr$getNextFeature()
#> OGR feature
#> $FID
#> integer64
#> [1] 61
#>
#> $event_id
#> [1] WY4438911082120200822
#>
#> $incid_name
#> [1] LONE STAR
#>
#> $incid_type
#> [1] Wildfire
#>
#> $map_id
#> integer64
#> [1] 10020495
#>
#> $burn_bnd_ac
#> integer64
#> [1] 3348
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lat
#> [1] 44.4
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lon
#> [1] -110.782
#>
#> $ig_date
#> [1] 2020-08-22
#>
#> $ig_year
#> [1] 2020
#>
#> $geom
#> [1] WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#>
## clear the attribute filter
lyr$setAttributeFilter("")
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 61
## set a spatial filter
## get the bounding box of the largest 1988 fire and use as spatial filter
## first set a temporary attribute filter to do the lookup
lyr$setAttributeFilter("ig_year = 1988 ORDER BY burn_bnd_ac DESC")
(feat <- lyr$getNextFeature())
#> OGR feature
#> $FID
#> integer64
#> [1] 7
#>
#> $event_id
#> [1] WY4470811082119880722
#>
#> $incid_name
#> [1] NORTH FORK
#>
#> $incid_type
#> [1] Wildfire
#>
#> $map_id
#> integer64
#> [1] 10014217
#>
#> $burn_bnd_ac
#> integer64
#> [1] 563527
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lat
#> [1] 44.678
#>
#> $burn_bnd_lon
#> [1] -110.716
#>
#> $ig_date
#> [1] 1988-07-22
#>
#> $ig_year
#> [1] 1988
#>
#> $geom
#> [1] WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#>
bbox <- g_wk2wk(feat$geom) |> bbox_from_wkt()
## set spatial filter on the full layer
lyr$setAttributeFilter("") # clears the attribute filter
lyr$setSpatialFilterRect(bbox)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 40
## fetch in chunks and return as data frame (class OGRFeatureSet)
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
head(feat_set)
#> OGR feature set
#> FID event_id incid_name incid_type map_id
#> 1 38 MT4471311115120070627 MADISON ARM Wildfire 16113
#> 2 7 WY4470811082119880722 NORTH FORK Wildfire 10014217
#> 3 32 MT4491211108020030820 RATHBONE Wildfire 13014
#> 4 25 WY4433011103020000816 SPRUCE COMPLEX (PLATEAU) Wildfire 10014141
#> 5 6 WY4499211096519880625 FAN Wildland Fire Use 10014215
#> 6 40 MT4502711102920070720 OWL Wildfire 16428
#> burn_bnd_ac burn_bnd_lat burn_bnd_lon ig_date ig_year
#> 1 3564 44.713 -111.151 2007-06-27 2007
#> 2 563527 44.678 -110.716 1988-07-22 1988
#> 3 2701 44.912 -111.080 2003-08-20 2003
#> 4 2808 44.329 -111.027 2000-08-16 2000
#> 5 20422 44.994 -110.976 1988-06-25 1988
#> 6 2175 45.027 -111.029 2007-07-20 2007
#> geom
#> 1 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 2 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 3 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 4 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 5 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
#> 6 WKB MULTIPOLYGON: raw 01 06 00 00 ...
plot(feat_set)
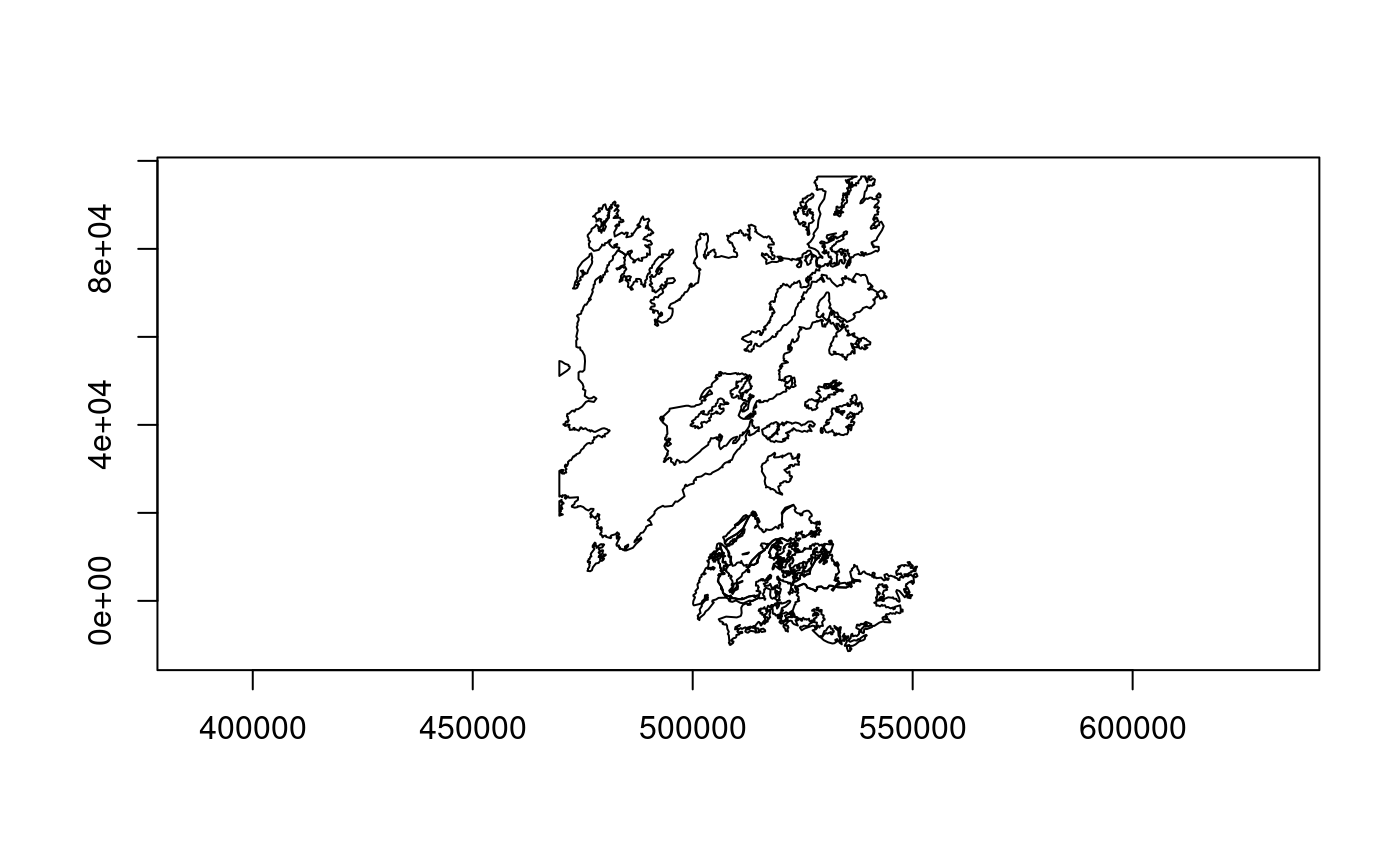 ## the next chunk
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 20
## no features remaining
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 0
str(feat_set) # 0-row data frame with columns fully typed
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 0 obs. of 11 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64
#> $ event_id : chr
#> $ incid_name : chr
#> $ incid_type : chr
#> $ map_id :integer64
#> $ burn_bnd_ac :integer64
#> $ burn_bnd_lat: chr
#> $ burn_bnd_lon: chr
#> $ ig_date : 'Date' num(0)
#> $ ig_year : int
#> $ geom : list()
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "MULTIPOLYGON"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "PROJCS[\"NAD83 / Montana\",GEOGCS[\"NAD83\",DATUM[\"North_American_Datum_1983\",SPHEROID[\"GRS 1980\",6378137,2"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
## or, fetch all pending features from the beginning
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1) # resets reading to the first feature
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 40
plot(feat_set)
## the next chunk
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 20
## no features remaining
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(20)
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 0
str(feat_set) # 0-row data frame with columns fully typed
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 0 obs. of 11 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64
#> $ event_id : chr
#> $ incid_name : chr
#> $ incid_type : chr
#> $ map_id :integer64
#> $ burn_bnd_ac :integer64
#> $ burn_bnd_lat: chr
#> $ burn_bnd_lon: chr
#> $ ig_date : 'Date' num(0)
#> $ ig_year : int
#> $ geom : list()
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "MULTIPOLYGON"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "PROJCS[\"NAD83 / Montana\",GEOGCS[\"NAD83\",DATUM[\"North_American_Datum_1983\",SPHEROID[\"GRS 1980\",6378137,2"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
## or, fetch all pending features from the beginning
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1) # resets reading to the first feature
nrow(feat_set)
#> [1] 40
plot(feat_set)
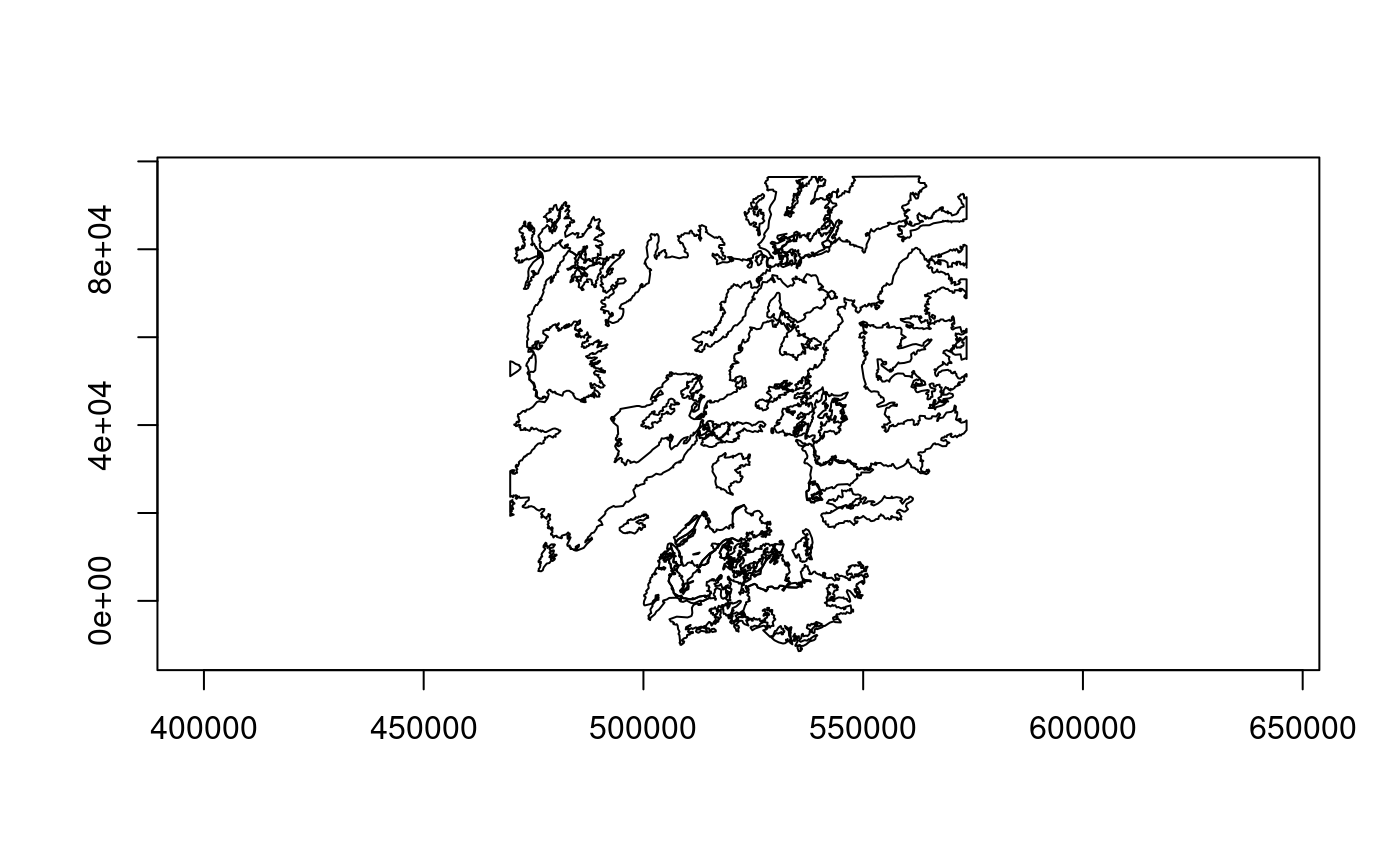 lyr$clearSpatialFilter()
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 61
lyr$close()
## simple example of feature write methods showing use of various data types
## create and write to a new layer in a GeoPackage data source
dsn2 <- tempfile(fileext = ".gpkg")
## define a feature class
defn <- ogr_def_layer("POINT", srs = epsg_to_wkt(4326))
## add field definitions
defn$unique_int <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger", is_nullable = FALSE,
is_unique = TRUE)
defn$bool_data <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger", fld_subtype = "OFSTBoolean")
defn$large_ints <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger64")
defn$doubles <- ogr_def_field("OFTReal")
defn$strings <- ogr_def_field("OFTString", fld_width = 50)
defn$dates <- ogr_def_field("OFTDate")
defn$dt_modified <- ogr_def_field("OFTDateTime",
default_value = "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP")
defn$blobs <- ogr_def_field("OFTBinary")
lyr <- ogr_ds_create("GPKG", dsn2, "test_layer", layer_defn = defn,
return_obj = TRUE)
# lyr$getLayerDefn() |> str()
## define a feature to write
feat1 <- list()
# $FID is omitted since it is assigned when written (could also be NA)
# $dt_modified is omitted since a default timestamp is defined on the field
feat1$unique_int <- 1001
feat1$bool_data <- TRUE
# pass a string to as.integer64() since the value is too large to be
# represented exactly as an R numeric value (i.e., double)
feat1$large_ints <- bit64::as.integer64("90071992547409910")
feat1$doubles <- 1.234
feat1$strings <- "A test string"
feat1$dates <- as.Date("2025-01-01")
feat1$blobs <- charToRaw("A binary object")
feat1$geom <- "POINT (1 1)" # can be a WKT string or raw vector of WKB
## create as a new feature in the layer
lyr$createFeature(feat1)
#> [1] TRUE
## get the assigned FID
lyr$getLastWriteFID()
#> integer64
#> [1] 1
## attempt to re-write the same feature fails due to the unique constraint
lyr$createFeature(feat1)
#> GDAL FAILURE 1: failed to execute insert : UNIQUE constraint failed: test_layer.unique_int
#> [1] FALSE
feat2 <- list()
feat2$unique_int <- 1002
feat2$bool_data <- FALSE
feat2$large_ints <- bit64::as.integer64("90071992547409920")
feat2$doubles <- 2.345
feat2$strings <- "A test string 2"
feat2$dates <- as.Date("2024-01-02")
feat2$blobs <- charToRaw("A binary object 2")
feat2$geom <- "POINT (2 2)"
lyr$createFeature(feat2)
#> [1] TRUE
lyr$getLastWriteFID()
#> integer64
#> [1] 2
## close and re-open as a read-only layer
lyr$open(read_only = TRUE)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 2
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1) # -1 to fetch all features from the beginning
str(feat_set)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 2 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 1 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1001 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi TRUE FALSE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409910 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 1.23 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string" "A test string 2"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2025-01-01" "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01" "2025-12-03 18:07:01"
#> $ blobs :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
## edit an existing feature, e.g., feat <- lyr$getFeature(2)
## here we copy a row of the data frame returned by lyr$fetch() above
feat <- feat_set[2,]
str(feat)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 1 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi FALSE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string 2"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01"
#> $ blobs :List of 1
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom :List of 1
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
Sys.sleep(1) # to ensure a timestamp difference
feat$bool_data <- TRUE
feat$strings <- paste(feat$strings, "- edited")
feat$dt_modified <- Sys.time()
feat$geom <- "POINT (2.001 2.001)"
lyr$open(read_only = FALSE)
## lyr$setFeature() re-writes the feature identified by the $FID element
lyr$setFeature(feat)
#> [1] TRUE
lyr$open(read_only = TRUE)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 2
lyr$returnGeomAs <- "WKT"
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1)
str(feat_set)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 2 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 1 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1001 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi TRUE TRUE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409910 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 1.23 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string" "A test string 2 - edited"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2025-01-01" "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01" "2025-12-03 18:07:02"
#> $ blobs :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom : chr "POINT (1 1)" "POINT (2.001 2.001)"
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKT"
lyr$close()
## Arrow array stream exposed as a nanoarrow_array_stream object
## requires GDAL >= 3.6
if (gdal_version_num() >= gdal_compute_version(3, 6, 0)) {
sql <- "SELECT incid_name, geom from mtbs_perims LIMIT 5"
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, sql)
stream <- lyr$getArrowStream()
# disable a warning for the example that can be safely ignored here
options(nanoarrow.warn_unregistered_extension = FALSE)
# pull all the batches into a data frame
d <- as.data.frame(stream)
# the geometry column is a list column of WKB raw vectors, which can be
# passed to the Geometry API g_*() functions, e.g.,
g_centroid(d$geom) |> print()
# release the stream when finished
stream$release()
lyr$close()
}
#> x y
#> [1,] 504185.6 -11945.72
#> [2,] 534834.7 86727.91
#> [3,] 553856.8 89236.52
#> [4,] 556496.3 51930.36
#> [5,] 557768.3 42471.93
lyr$clearSpatialFilter()
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 61
lyr$close()
## simple example of feature write methods showing use of various data types
## create and write to a new layer in a GeoPackage data source
dsn2 <- tempfile(fileext = ".gpkg")
## define a feature class
defn <- ogr_def_layer("POINT", srs = epsg_to_wkt(4326))
## add field definitions
defn$unique_int <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger", is_nullable = FALSE,
is_unique = TRUE)
defn$bool_data <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger", fld_subtype = "OFSTBoolean")
defn$large_ints <- ogr_def_field("OFTInteger64")
defn$doubles <- ogr_def_field("OFTReal")
defn$strings <- ogr_def_field("OFTString", fld_width = 50)
defn$dates <- ogr_def_field("OFTDate")
defn$dt_modified <- ogr_def_field("OFTDateTime",
default_value = "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP")
defn$blobs <- ogr_def_field("OFTBinary")
lyr <- ogr_ds_create("GPKG", dsn2, "test_layer", layer_defn = defn,
return_obj = TRUE)
# lyr$getLayerDefn() |> str()
## define a feature to write
feat1 <- list()
# $FID is omitted since it is assigned when written (could also be NA)
# $dt_modified is omitted since a default timestamp is defined on the field
feat1$unique_int <- 1001
feat1$bool_data <- TRUE
# pass a string to as.integer64() since the value is too large to be
# represented exactly as an R numeric value (i.e., double)
feat1$large_ints <- bit64::as.integer64("90071992547409910")
feat1$doubles <- 1.234
feat1$strings <- "A test string"
feat1$dates <- as.Date("2025-01-01")
feat1$blobs <- charToRaw("A binary object")
feat1$geom <- "POINT (1 1)" # can be a WKT string or raw vector of WKB
## create as a new feature in the layer
lyr$createFeature(feat1)
#> [1] TRUE
## get the assigned FID
lyr$getLastWriteFID()
#> integer64
#> [1] 1
## attempt to re-write the same feature fails due to the unique constraint
lyr$createFeature(feat1)
#> GDAL FAILURE 1: failed to execute insert : UNIQUE constraint failed: test_layer.unique_int
#> [1] FALSE
feat2 <- list()
feat2$unique_int <- 1002
feat2$bool_data <- FALSE
feat2$large_ints <- bit64::as.integer64("90071992547409920")
feat2$doubles <- 2.345
feat2$strings <- "A test string 2"
feat2$dates <- as.Date("2024-01-02")
feat2$blobs <- charToRaw("A binary object 2")
feat2$geom <- "POINT (2 2)"
lyr$createFeature(feat2)
#> [1] TRUE
lyr$getLastWriteFID()
#> integer64
#> [1] 2
## close and re-open as a read-only layer
lyr$open(read_only = TRUE)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 2
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1) # -1 to fetch all features from the beginning
str(feat_set)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 2 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 1 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1001 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi TRUE FALSE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409910 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 1.23 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string" "A test string 2"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2025-01-01" "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01" "2025-12-03 18:07:01"
#> $ blobs :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
## edit an existing feature, e.g., feat <- lyr$getFeature(2)
## here we copy a row of the data frame returned by lyr$fetch() above
feat <- feat_set[2,]
str(feat)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 1 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi FALSE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string 2"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01"
#> $ blobs :List of 1
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom :List of 1
#> ..$ : raw 01 01 00 00 ...
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKB"
Sys.sleep(1) # to ensure a timestamp difference
feat$bool_data <- TRUE
feat$strings <- paste(feat$strings, "- edited")
feat$dt_modified <- Sys.time()
feat$geom <- "POINT (2.001 2.001)"
lyr$open(read_only = FALSE)
## lyr$setFeature() re-writes the feature identified by the $FID element
lyr$setFeature(feat)
#> [1] TRUE
lyr$open(read_only = TRUE)
lyr$getFeatureCount()
#> [1] 2
lyr$returnGeomAs <- "WKT"
feat_set <- lyr$fetch(-1)
str(feat_set)
#> Classes ‘OGRFeatureSet’ and 'data.frame': 2 obs. of 10 variables:
#> $ FID :integer64 1 2
#> $ unique_int : int 1001 1002
#> $ bool_data : logi TRUE TRUE
#> $ large_ints :integer64 90071992547409910 90071992547409920
#> $ doubles : num 1.23 2.35
#> $ strings : chr "A test string" "A test string 2 - edited"
#> $ dates : Date, format: "2025-01-01" "2024-01-02"
#> $ dt_modified: POSIXct, format: "2025-12-03 18:07:01" "2025-12-03 18:07:02"
#> $ blobs :List of 2
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> ..$ : raw 41 20 62 69 ...
#> $ geom : chr "POINT (1 1)" "POINT (2.001 2.001)"
#> - attr(*, "gis")=List of 5
#> ..$ type : chr "vector"
#> ..$ geom_column : chr "geom"
#> ..$ geom_col_type: chr "POINT"
#> ..$ geom_col_srs : chr "GEOGCS[\"WGS 84\",DATUM[\"WGS_1984\",SPHEROID[\"WGS 84\",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY[\"EPSG\",\"7030\"]],AU"| __truncated__
#> ..$ geom_format : chr "WKT"
lyr$close()
## Arrow array stream exposed as a nanoarrow_array_stream object
## requires GDAL >= 3.6
if (gdal_version_num() >= gdal_compute_version(3, 6, 0)) {
sql <- "SELECT incid_name, geom from mtbs_perims LIMIT 5"
lyr <- new(GDALVector, dsn, sql)
stream <- lyr$getArrowStream()
# disable a warning for the example that can be safely ignored here
options(nanoarrow.warn_unregistered_extension = FALSE)
# pull all the batches into a data frame
d <- as.data.frame(stream)
# the geometry column is a list column of WKB raw vectors, which can be
# passed to the Geometry API g_*() functions, e.g.,
g_centroid(d$geom) |> print()
# release the stream when finished
stream$release()
lyr$close()
}
#> x y
#> [1,] 504185.6 -11945.72
#> [2,] 534834.7 86727.91
#> [3,] 553856.8 89236.52
#> [4,] 556496.3 51930.36
#> [5,] 557768.3 42471.93